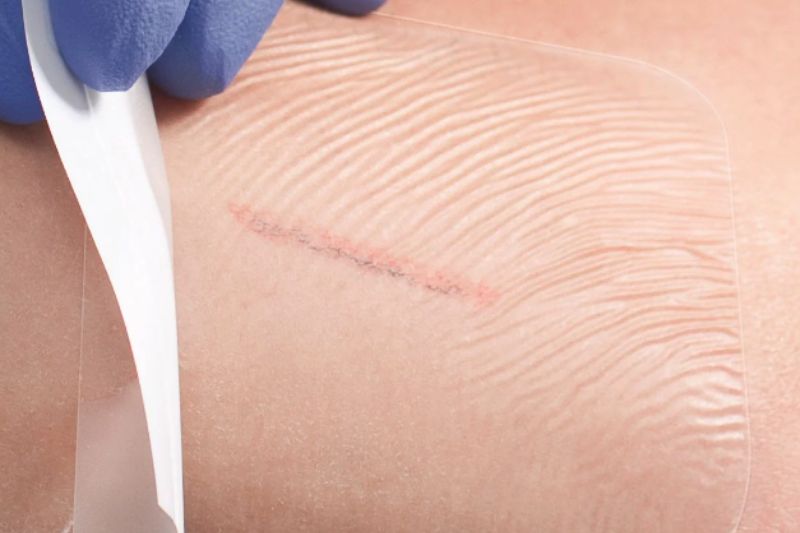
Alginate Dressings
Made from seaweed-derived fibers, these dressings are highly absorbent and are commonly used for wounds with moderate to heavy exudate.


Hydrocolloid Dressings
These dressings can absorb wound fluid to form a gel, creating a moist environment that promotes healing. They are ideal for low to moderately exuding wounds.


Foam Dressings
These dressings feature a soft, absorbent foam layer, making them perfect for wounds with moderate exudate. They offer insulation and help maintain a moist healing environment.


Transparent Films
Thin and transparent, these dressings enable visual inspection of the wound without the need to remove them. They are commonly used for superficial wounds or to secure primary dressings in place.


Silver Dressings
Infused with silver, these dressings possess antimicrobial properties and are used to prevent or control infections in wounds.


Collagen Dressings
Collagen dressings, derived from animal or human sources, support tissue growth and are commonly used for chronic wounds.


Composite Dressings
These dressings combine various materials to offer multiple benefits, including absorption, moisture control, and bacterial protection.


Non-Adherent Dressings
Non-adherent dressings are designed to minimize trauma during dressing changes, making them ideal for wounds with fragile or sensitive tissue.


Honey-based Dressings
Use medical-grade honey, recognized for its antimicrobial and healing properties. It is effective for treating infected wounds, burns, and wounds with delayed healing.


Topical Antibiotics
Antibiotic ointments or creams are applied directly to the wound to prevent or treat infections. They are used for infected wounds or as a preventive measure in specific cases.


Antiseptic Solutions
Antiseptic solutions, such as iodine or chlorhexidine, are applied to wounds for disinfection. They are used for cleansing wounds and preventing infection.


Barrier Films
Thin, transparent films form a protective barrier over the wound, safeguarding against friction, shear, and moisture in superficial wounds.


Enzymatic Debriding Agents
Enzymatic agents break down necrotic tissue in wounds, aiding in the debridement process. They are particularly useful for chronic wounds containing necrotic tissue.

The selection of a dressing or topical treatment depends on factors such as the wound type, stage, exudate level, presence of infection, and the overall wound management plan. Healthcare professionals evaluate the wound to choose the most suitable dressing or treatment, ensuring effective care tailored to each patient's unique condition.